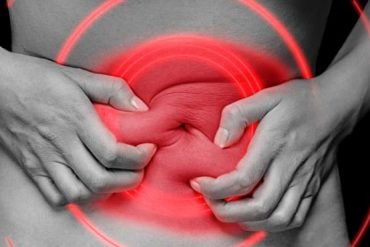
1. Pain and Cramping
The most common symptom of IBS is abdominal pain and cramping, which is usually the most important factor for diagnosis. Your brain and gut will work together to control digestion. This will take place through the hormones, signals, and nerves that the good bacteria living in your gut will release.
When you have IBS, the signals will be distorted and will result in painful tensions on the muscles of your digestive tract, which is the reason behind the pain and cramping. The pain will usually occur at the lower abdomen and will sometimes spread to the entire abdomen. However, it is less likely to affect only the upper abdomen. The pain will eventually subside after a bowel movement.
Diet modifications, which consist of eating foods that are low in FODMAPs, can help improve the pain. Doctors will also prescribe other treatments, such a bowel relaxants, including peppermint oil. Cognitive behavior therapy and hypnotherapy may also help to ease the pain.
But if the pain does not respond to any of these treatments, a gastroenterologist can look for a medication that can specifically ease your IBS pain.