Cytokine Proteins and Fibromyalgia?
Studies till date have found conflicting results in the relationship between cytokine protein and fibromyalgia. While some suggest that there is no direct link between the two, other studies suggest that abnormal levels of cytokine protein play a part in elevated pain and may even cause fibromyalgia.
| Sponsored Links |
|
|
What Are Cytokine Protein?
Before we go into discussion on the studies linking cytokine protein to fibromyalgia, it is important to first understand what are cytokine proteins are and how they can influence pain.
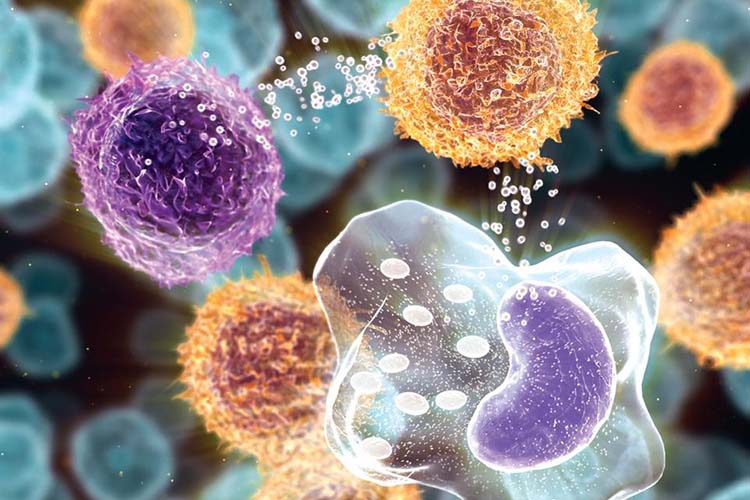
Cytokine protein plays a crucial role in our immune system. It helps to control the activity, growth and death of the immune cells in our body. In other words, to maintain a healthy functioning immune system, having healthy levels of cytokine proteins is essential. In an event of an infection or virus attack, cytokine helps to activate our white blood cells to fight against the harmful substances, a process known as inflammation. During inflammation, your body can experience pain, discomfort, heat and redness.
Cytokine proteins can either be proinflammatory or anti-inflammatory. This means that increased levels of proinflammatory cytokine proteins and reduced levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine proteins can both increase pain.
Proinflammatory cytokines include: interleukin 1α (IL- 1α), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), interleukin 2 (IL-2), interleukin 6 (IL-6), interleukin 8 (IL-8), and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α).
Anti- inflammatory cytokines include: interleukin 4 (IL-4), interleukin 10 (IL-10), and interleukin 13 (IL-13).
| Sponsored Links |
|
|